Welcome back. Today, we’re talking about the third theory of emotion. This one is about the Two-Factor theory.
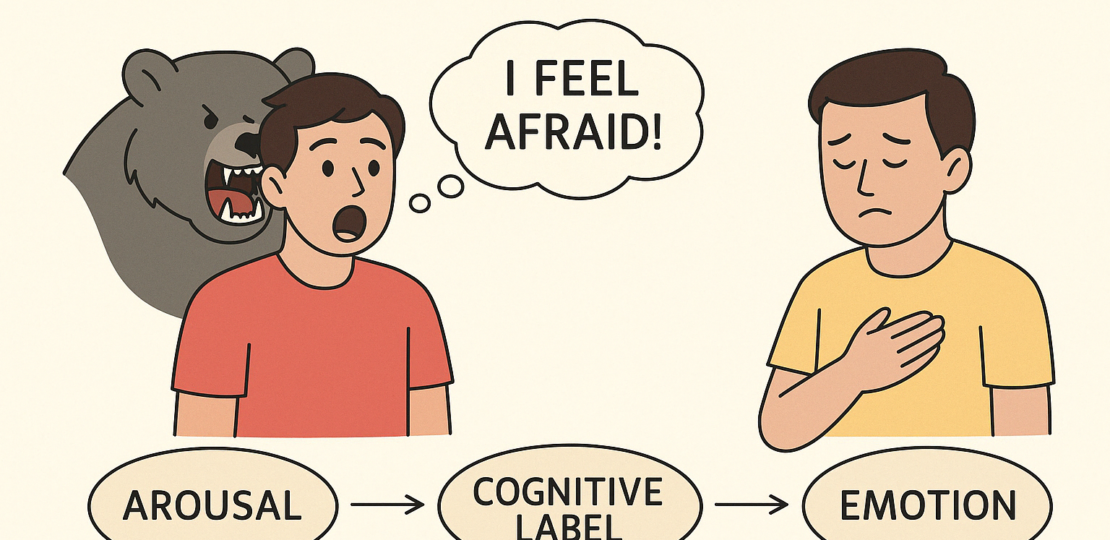
If we think about physical expressions of emotions, can we actually tell the difference between emotions? We actually cannot. Think about this for a second. What’s the difference between feeling nervous and excited? Both increase heartbeat, cause perspiration, etc. So, how do you tell the difference? According to the Schachter-Singer Theory of Emotion, it all comes down to how you interpret what’s happening. Developed by Stanley Schachter and Jerome Singer in 1962, this theory, also called the Two-Factor Theory of Emotion, proposes that emotions are the result of a combination of physiological arousal and cognitive interpretation.
Let’s say your heart is racing. On its own, that could mean anything—fear, excitement, love. But if you just aced a test, your brain labels the feeling as happiness or pride. If you’re walking down a dark alley, that same physical reaction might be labeled as fear. The takeaway? The body sends a general alert signal, and the brain decides what it means.
Their classic experiment involved injecting participants with adrenaline (to create physical arousal) and then placing them in different social situations. Depending on whether the environment was playful or hostile, the participants reported feeling either euphoric or angry. This showed that the interpretation of the situation shaped their emotional experience.
The Schachter-Singer theory underscores how emotions are shaped not only by our biology but also by our thoughts and perceptions. It’s a powerful reminder that how we think about what’s happening often determines how we feel. Now, as I finish this post, I realize how similar the theories sound. Believe it or not, they are that similar in reality. Minute differences separate them, but these separations are necessary to explain various situations we as humans encounter. A single theory cannot explain everything; hence, we talk about different theories and apply different ones to different scenarios.
RELATED POSTS
View all

